GHRP-2 is a synthetic growth hormone secretagogue that binds to the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor. It has been shown in research trials to improve muscle growth, regulate the immune system, and improve sleep cycles.

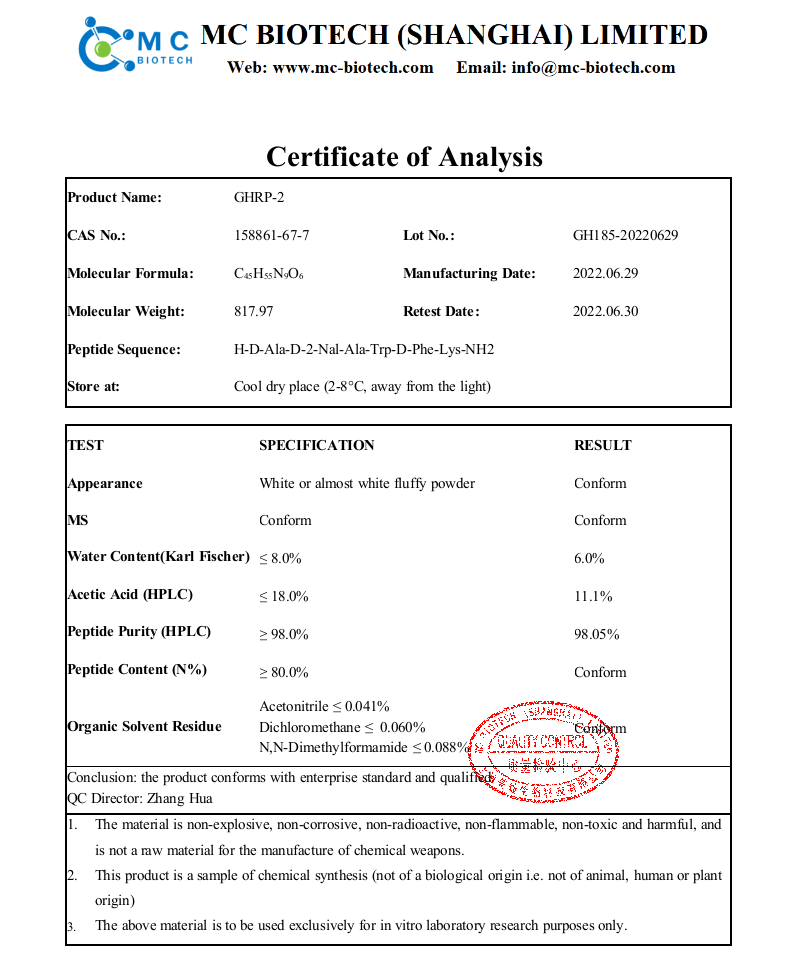
Name: GHRP-2; Pralmorelin
CAS No.: 158861-67-7
Peptide Sequence: H-D-Ala-D-2-Nal-Ala-Trp-D-Phe-Lys-NH2
Molecular Formula: C45H55N9O6
Molecular Weight: 817.97
Appearance: White Lyophilized powder
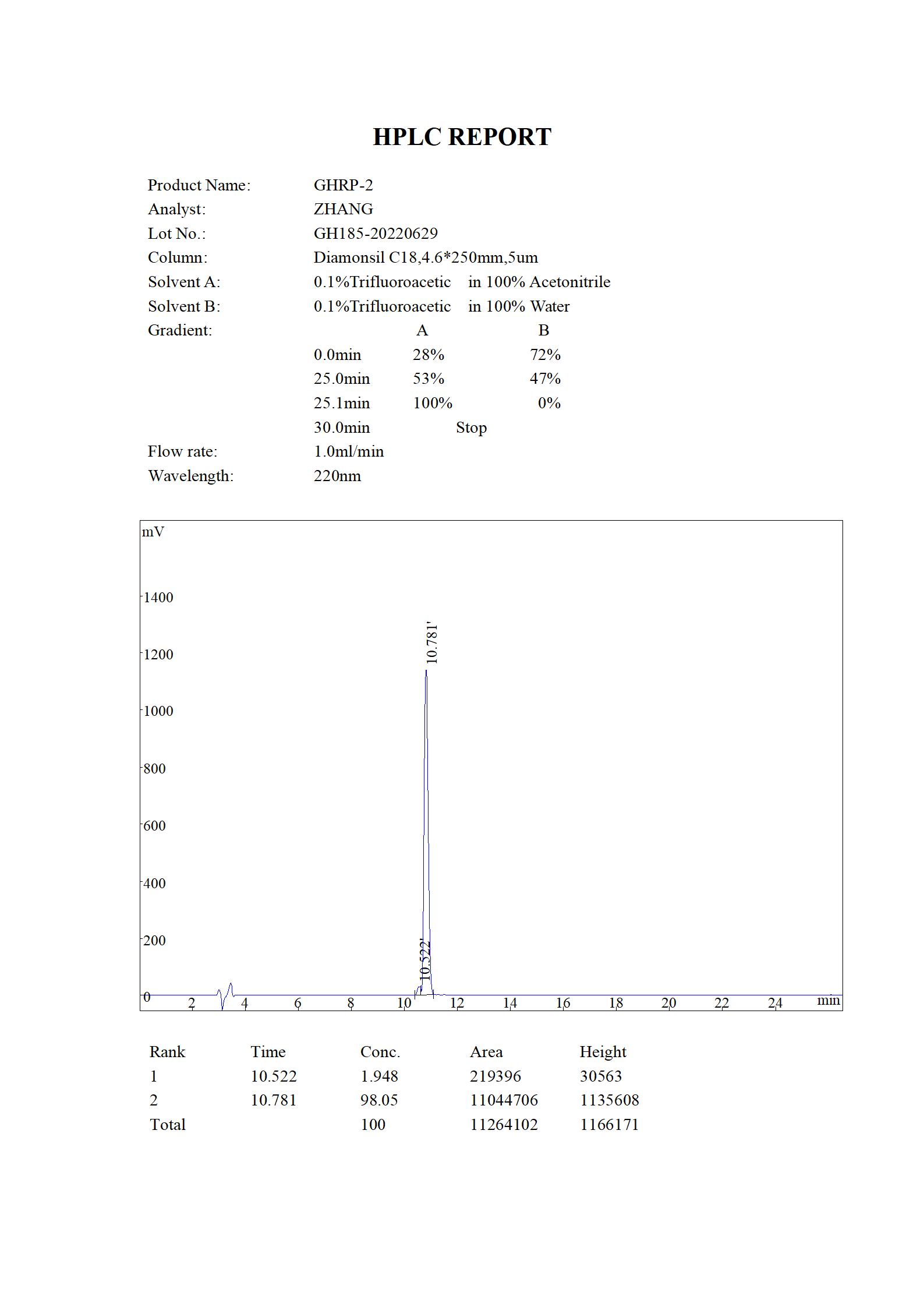
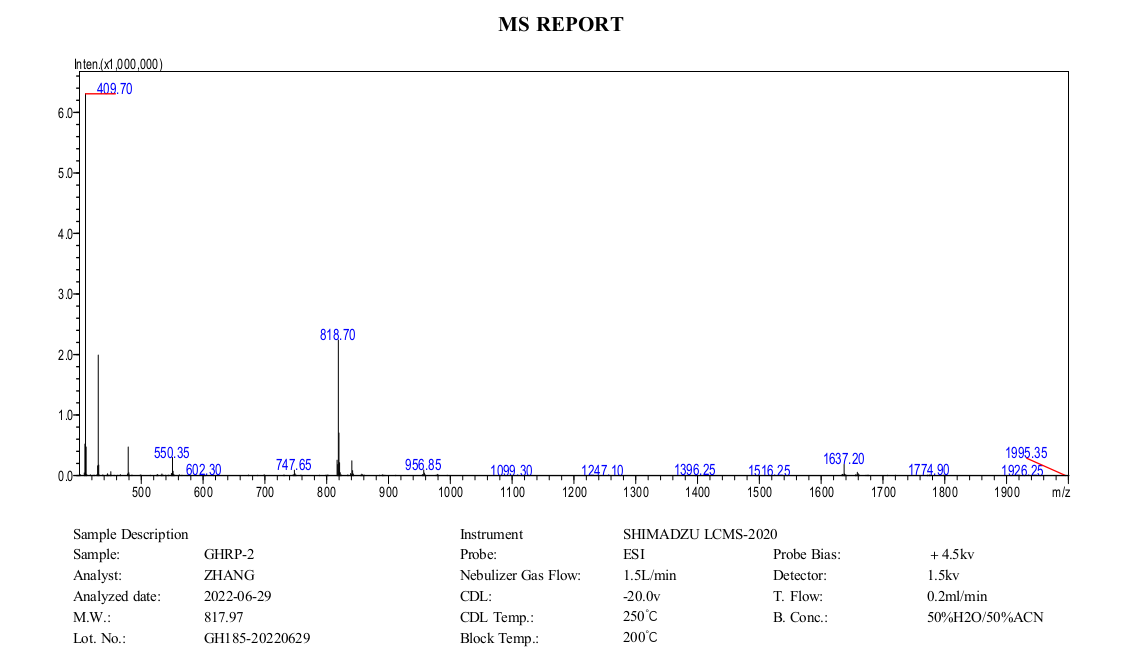
GHRP-2 (a.k.a. pralmorelin) is a synthetic growth hormone secretagogue known to bind to the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor. It was the first of the growth hormone secretagogues to be introduced and is currently marketed as a test peptide for the assessment of growth hormone deficiency and secondary adrenal failure. GHRP-2 has been investigated in stage II clinical trials for the assessment of short stature and is under active research for its effects on appetite, muscle growth, the immune system, and sleep cycles. GHRP-2 is orally and sublingually active, so it does not have to be injected to have its effects
Research in Yaks indicates that GHRP-2 can boost muscle growth in two ways: increased protein deposition and decreased protein degradation. The research showed that GHRP-2 can overcome natural growth plateaus that occur in yaks due to food deprivation, disease, and adverse environmental conditions (e.g. cold). The most profound finding from this study is that GHRP-2 reduces muscle atrophy by inactivating atrogin-1 and MuRF1, proteins that control the muscle degradation pathway. There is hope that these findings could be used to reduce the catabolism common in chronic illnesses like autoimmune disease, cancer, and more.
Of course, by activating growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1, GHRP-2 helps to boost muscle protein deposition. The combined effect of reducing degradation and enhancing deposition is that GHRP-2 encourages the development of lean body mass even in adverse conditions.
GHRP-2 has been shown to boost food intake. Though this may not seem acutely important, appetite stimulation in the setting of chronic disease is an important part of overall health care. The ability to easily and reliably stimulate appetite could help doctors treat chronically ill patients and improve long-term outcomes.

Food intake in healthy adult men, placebo versus GHRP-2
Source: PubMed
Research in fetal heart cell culture lines shows that GHRP-2 and its analogues (GHRP-1 and GHRP-6) can help to protect heart cells by reducing apoptosis or programmed cell death. This is of particular importance following heart attack, when heart cells are particularly prone to apoptosis thanks to decreased blood and thus nutrient supply. Research using an analogue of GHRP-2 called Hexarelin has indicated that there may be a specific receptor for these peptides. Identifying new receptors in any tissue opens pathways for new drug development, but also deepens our understanding of the human physiology and how to prevent dysfunction in the first place.
GHRP-2 has been shown to stimulate the thymus, an organ responsible for protecting certain cells of the immune system. In particular., the thymus helps T cells to mature. T cells are critical for adaptive immunity and our ability to fight off complex infections. Function of the thymus declines with age, which leads to a number of age-related dysfunctions ranging from inadequate tissue repair to lost immunity and thus an inability to fight off infections, guard against cancer, and maintain normal tissue function. GHRP-2 has been shown to rejuvenate the thymus, boosting the number and diversity of T-cells it produces. This leads to improved immunity.

Change in number of active T-cells following administration of GHRP-2
Source: PubMed
GHRP-2 has been shown to increase the duration stages 3 and 4 of the sleep cycles by about 50% each while increasing REM sleep by approximately 20% while reducing the amount that an individual deviates from “normal sleep” by as much as a third. Overall, the improvement in sleep led to improvement in cognitive function, blood pressure, healing, and energy levels. These findings, while useful to all adults, are particularly important in the elderly, where the effects of aging take a toll on sleep quality. GHRP-2 may be useful in understanding how to fine-tune sleep to improve quality and maybe even help people get all the benefits of a full night’s sleep in a fraction of the time.
It was originally thought that observations of decreased pain in animal models of osteoarthritis were the result of GHRP-2 boosting growth hormone levels and accelerating healing in the damaged tissues. Keen scientists observed, however, that the pain relief preceded healing by a substantial margin, suggesting that GHRP-2 may have direct effects on pain perception. As it turns out, GHRP-2 has action at the opioid receptors.
There are four known opioid receptors. Most opioid pain medications do not discriminate between them. This is problematic because while some of the receptors mediate pain, others affect things like wakefulness and breathing while still others impact addiction. GHRP-2 is a selective opioid receptor agonist, binding primarily to the receptors responsible for pain relief, sedation, and addiction. This finding indicates that it may be possible to produce selective opioid agonists and therefore mitigate or prevent entirely undesirable effects like respiratory depression and addiction.
Product use: This product is only for research chemicals.
Contact: Sophia Wang
Phone:
E-mail: info@mc-biotech.com
Add: 2nd Floor,ECNU Science Park,No.1006 Jinshajiang Road, Putuo District, Shanghai