Hexarelin is a synthetic analogue of ghrelin that shows benefit in heart disease and cardiac ischemia, protecting the heart following heart attack. Research has shown that Hexarelin also protects skeletal muscle against wasting and improves cholesterol and triglyceride levels.

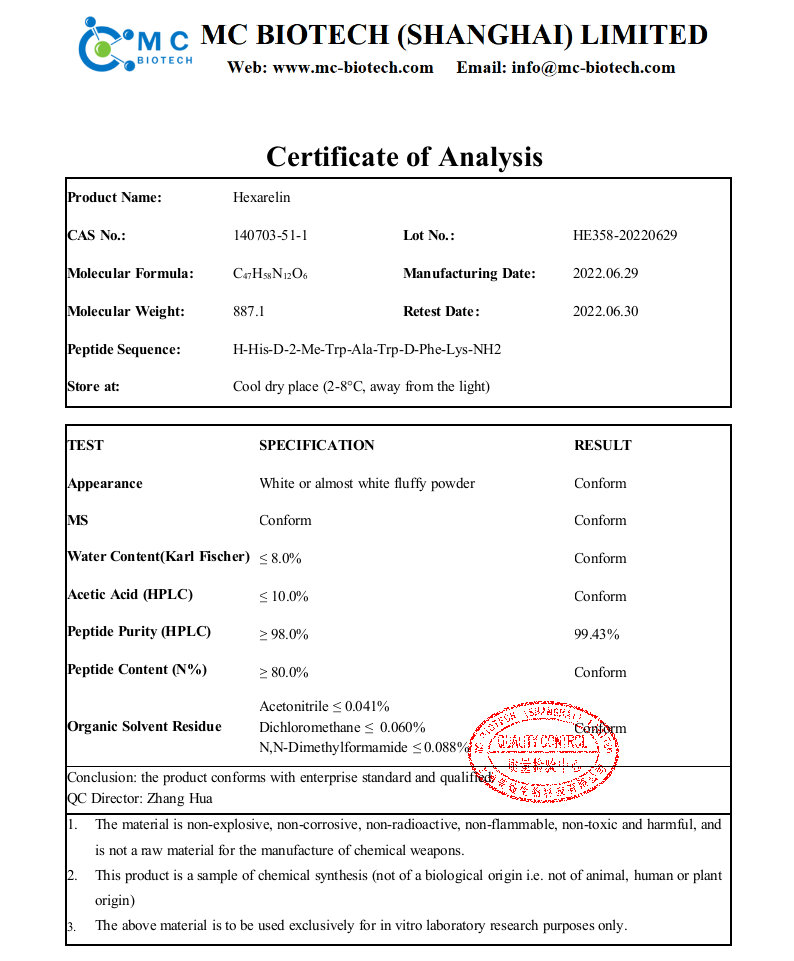
Name: Hexarelin; Examorelin
CAS No.: 140703-51-1
Peptide Sequence: His-D-2-Me-Trp-Ala-Trp-DPhe-Lys-NH2
Molecular Formula: C47H58N12O6
Molecular Weight: 887.04
Appearance: White Lyophilized powder
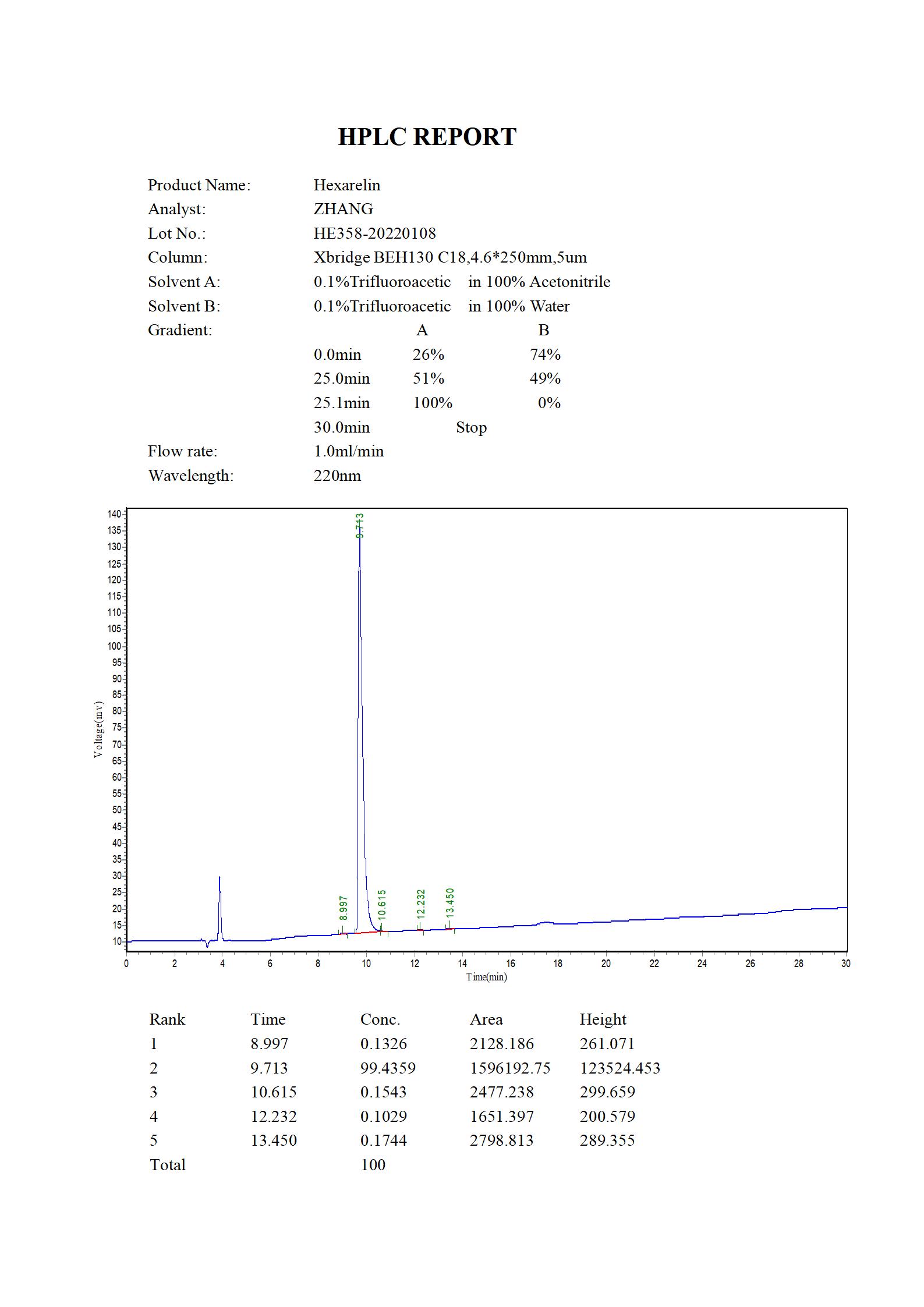
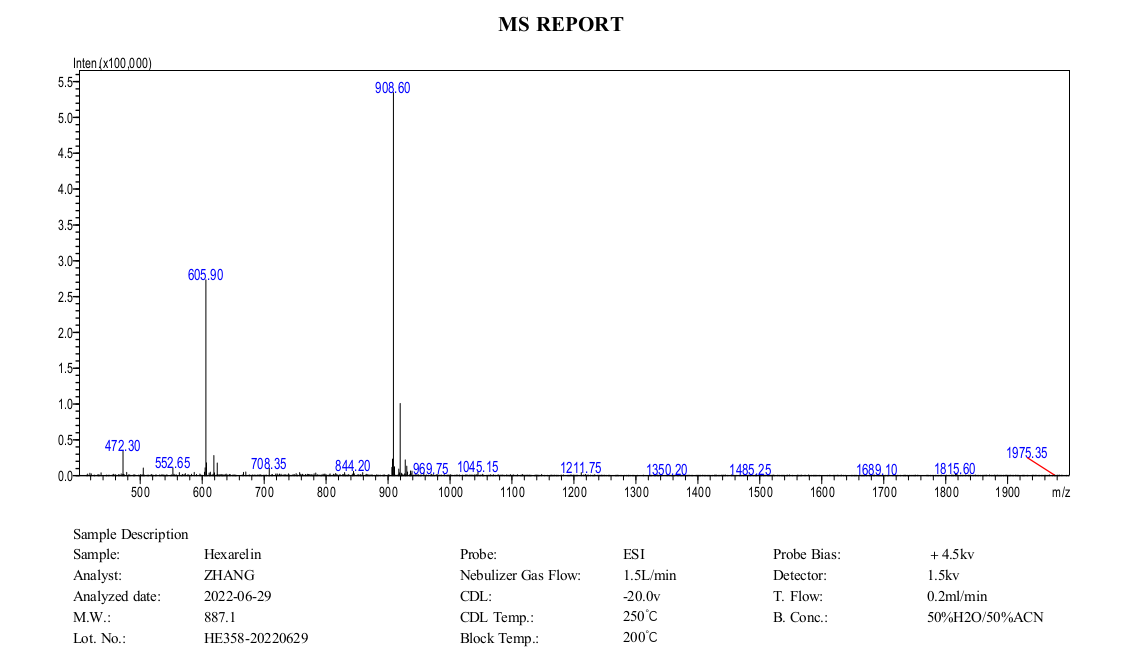
Hexarelin, also called Examorelin, is a synthetic analogue of ghrelin and is closely related to GHRP-6. In fact, hexarelin and GHRP-6 differ from each other only slightly thanks the addition of two methyl groups to GHRP-6. Hexarelin, like many ghrelin analogues, is orally and sublingually active and highly selective. Hexarelin has been heavily researched for its effects on heart cell survival following ischemia and nutrient deprivation.
Hexarelin directly affects the heart by binding to the CD36 receptor and the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR). Studies in mice suggest hexarelin protects heart cells from injury in the setting of heart attack by binding to these receptors and preventing cells from undergoing apoptosis (programmed cell death). Mice treated with hexarelin in this study showed improved heart function, increased number of surviving heart cells, and decreased production of malondialdehyde (a marker of heart cell death). Interestingly, GHRP-6 was found to be slightly superior to ghrelin in this study.
A study in rats investigating the ability of GHRP-6 to offset problems associated with heart failure found that the peptide reduces oxidative stress in heart failure and prevents myocardial remodeling from taking place. Remodeling is a pathological process associated with a decline in heart function and serious morbidity. Rats treated with GHRP-6 in this study had significant improvements in the function of their heart. These processes are thought to be mediated by GHRP-6 up-regulation of phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) activity as well as down regulation of protein kinase B expression. PTEN plays a role in cell regeneration while protein kinase B regulates cell survival.
GHRP-6 is so effective in reducing cardiac remodeling that it shifts the balance of nervous system activity away from sympathetic stimulation (higher heart rate, higher blood pressure, etc.) toward parasympathetic dominance. This not only improves short-term health and outcomes, but reduces the need for medication over the long term and likely helps to prevent cardiac remodeling that is secondary to increased stress on the heart. Rats treated with GHRP-6 following a heart attack show substantial reductions in the size of the scar left behind.
Because the mechanism by which hexarelin protects heart cells is not specific to the mechanism of damage in heart attack, researchers speculated that the peptide could be used to protect the heart from other insults as well. Research, again in rats, found that hexarelin improved cardiac function in a model of diabetes by changing the way calcium and potassium are processed by heart muscle cells.
Dyslipidemia refers to an abnormal amount of fat in the blood. Interestingly, dyslipidemia is an independent risk factor for the development of diabetes, even in thin and outwardly healthy individuals. In fact, dyslipidemia may help to explain the current diabetes crisis in first-world nations and understanding its effects on human physiology is paramount to combating the growing health concerns associated with modern diets. Research in rats indicates that GHRP-6 can correct dyslipidemia in the setting of insulin resistance (the first step in the pathway to diabetes) while simultaneously lowering blood sugar and insulin resistance. The peptide may offer an alternative to current lipid medications for the treatment of severe dyslipidemia.
It isn’t just heart muscle that hexarelin protects. Studies in rat models of cachexia (extreme weight loss due to illness or chemotherapy) indicate that GHRP-6 protects muscle cells by regulating calcium flow as well as mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondria are the power plants of cells. Without them, cells cannot produce the energy they need to carry out normal function and will eventually die.
Calcium regulation is often disrupted by chemotherapy. Calcium dysregulation is one of the primary reasons that muscle mass and lean body mass are affected during cancer treatment. Research in rats indicates GHRP-6 offsets the alterations in calcium regulation caused by chemotherapy.
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in most developed nations. Understanding the complex process that leads to heart disease, heart failure, and eventually death is not easy, but scientists are beginning to unravel the mystery with help from peptides like hexarelin. Research utilizing hexarelin has revealed a number of new pathways for understanding the function of the heart in health and disease. It has also opened the door to develop new treatments for problems, like cardiac remodeling, that have proved difficult to treat in the past.
Product use: This product is only for research chemicals.
Contact: Sophia Wang
Phone:
E-mail: info@mc-biotech.com
Add: 2nd Floor,ECNU Science Park,No.1006 Jinshajiang Road, Putuo District, Shanghai